Notes about Standardizing Live Migration with NVM Express
本文主要是mark下Standardizing Live Migration with NVM Express®相关notes,相关细节可以参考原文。
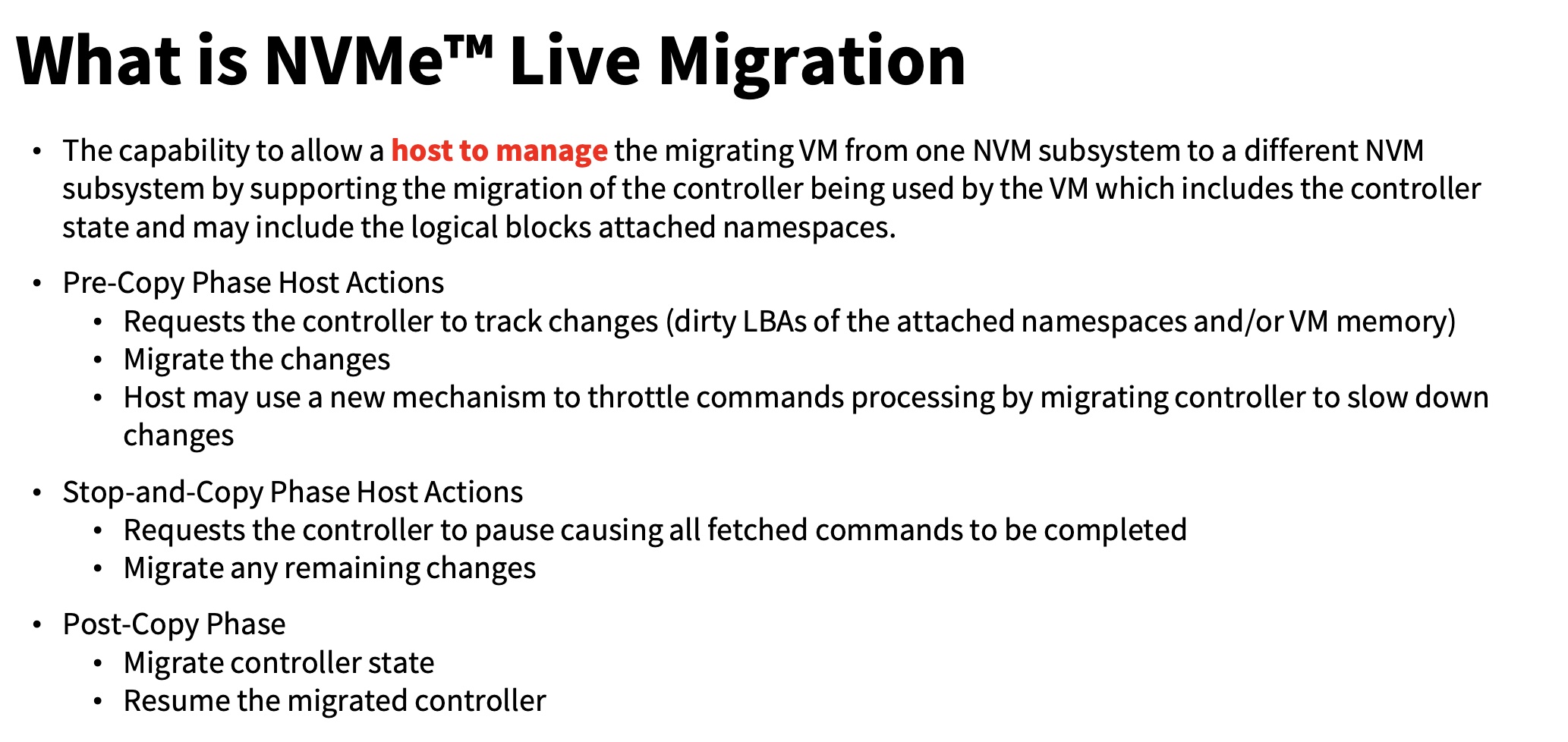
slides中有如下描述:
Host may use a new mechanism to throttle commands processing by migrating controller to slow down changes
其对应的是:
Support limit the BW and IOPS of a controller to allow slowing down of command processing on a migrating controller
这是QoS的相关实现,考虑写磁盘多的workload,不限速的话,最后一轮的脏LBAs可能会很多,downtime就会有些大了。
原文考虑了本地盘与非本地盘的NVMe Live Migration。
对于本地盘的情况,需要记录脏的LBAs,在热迁移每轮迭代中,会传输脏的LBAs(类似于热迁移的脏页传输)。
对于非本地盘的情况,其实就无效考虑脏的LBAs了。
对于IPU/DPU的NVMe Live Migration,详情可以参考NVMe VFIO Live Migration for IPU/DPU Devices。
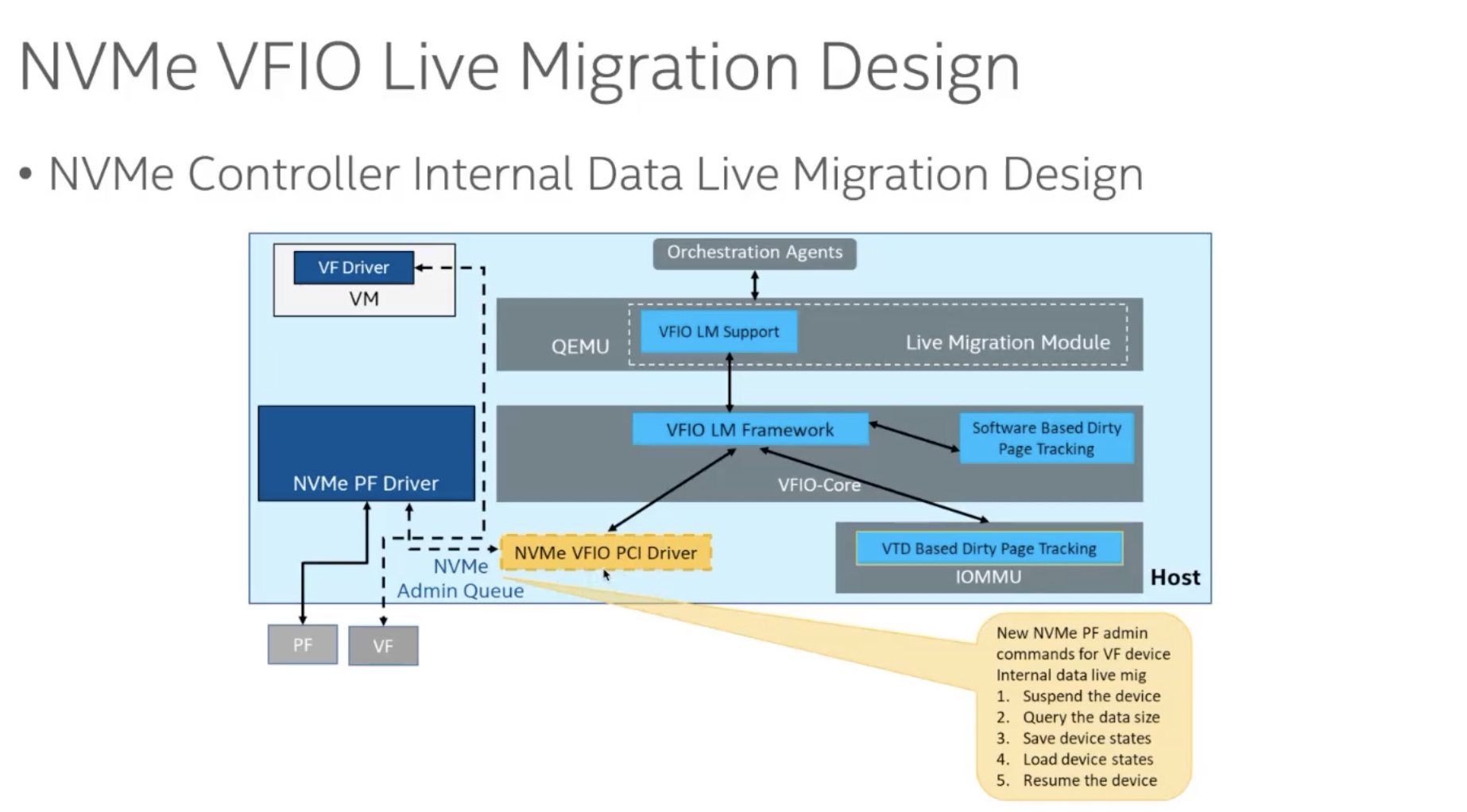
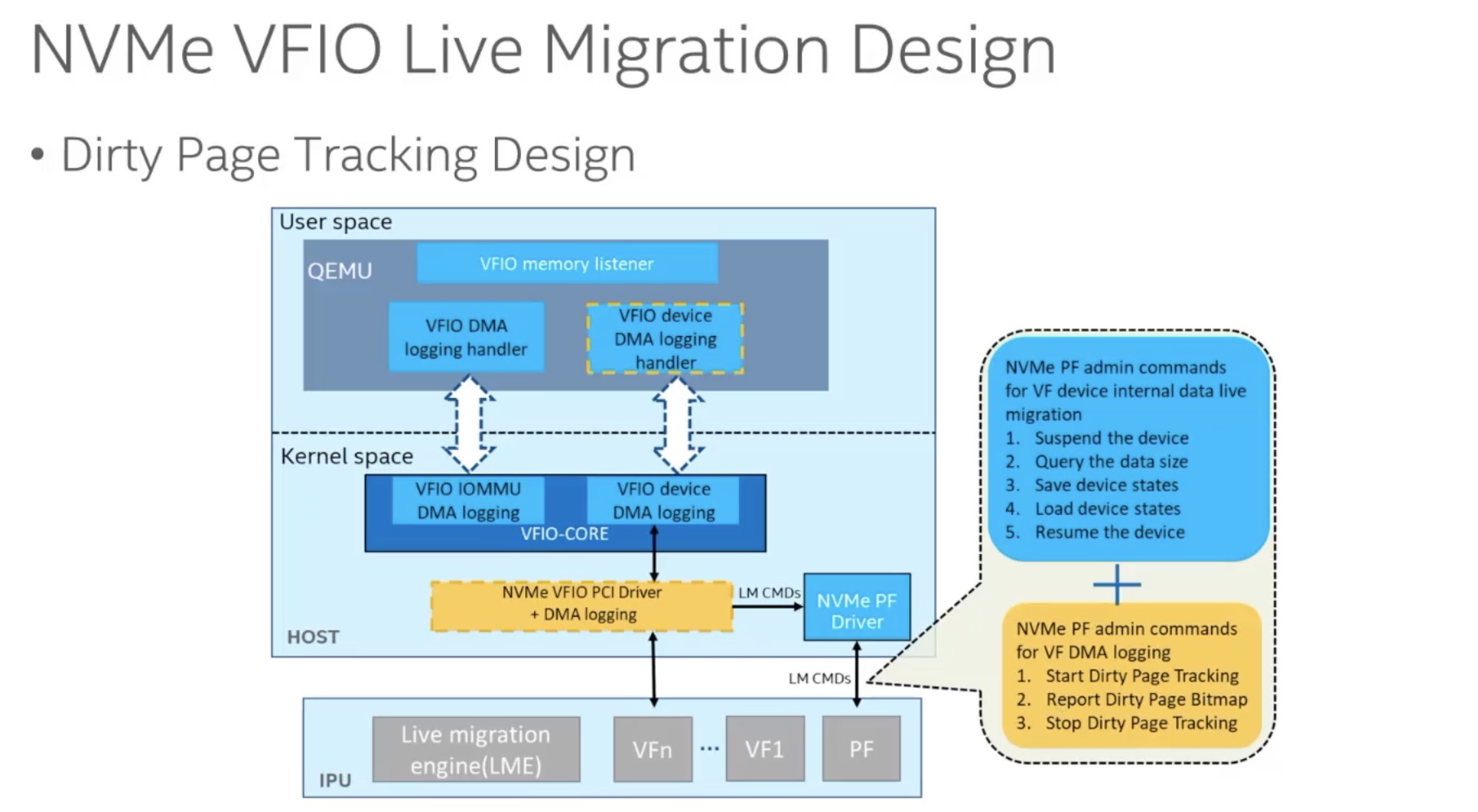
值得注意的是,如果host上的IOMMU支持DMA脏页记录的话,就无需NVMe Device自己去记录DMA脏页了。
参考资料: